Electrolytes are substances found in the body that affect its electrical balance. Electrolyte imbalances can lead to life-threatening health conditions, especially for people with chronic kidney disease or heart failure. Fortunately, for those of us without any underlying conditions, eating foods high in electrolytes is an easy way to maintain a healthy balance of these essential elements. In this article, we’ll cover the top 10 foods highest in electrolytes, along with their benefits for promoting good health.
Why Are Electrolytes Important?
An electrolyte is a substance that separates ions when dissolved in water that carries current in solution. Your brain, heart and muscles function because of electrolytes.
Ions are minerals that carry either a positive or negative charge which enables them to conduct electricity when dissolved in water. The most common electrolytes include:
- Sodium (Na+)
- Potassium (K+)
- Calcium (Ca2+)
- Chloride (Cl-)
- Bicarbonate(HCO3-)
- Magnesium (Mg2+)
- Phosphate (PO4 3-).
Electrolyte levels are mainly regulated by the kidneys. They keep an optimal balance between the ions for homeostasis. Sodium is one of the primary electrolytes that causes many health problems if levels get too high or low (12).
The good thing is that your body can easily handle changing levels of electrolytes because it has mechanisms in place to keep them within a safe range. If those mechanisms aren’t working correctly due to a chronic illness or dehydration, sodium can build up in your interstitial fluid, causing water retention. Excessive water retention leads to swelling of hands, face and legs which then becomes oedema (22).
Electrolytes help regulate the amount of water and other fluids in and around cells, as well as maintain the normal function of nerves and muscles. They also play a role in proper digestion and muscle contractions, including those that occur during exercise or periods of intense activity (10).
Read More: Detox Tea Facts, Health Benefits And Side Effects
Since electrolytes are found naturally in our bodies and the foods we eat, it’s important to maintain a sufficient supply of these substances. One way to do this is by eating foods that contain electrolytes, such as the top 10 listed below:
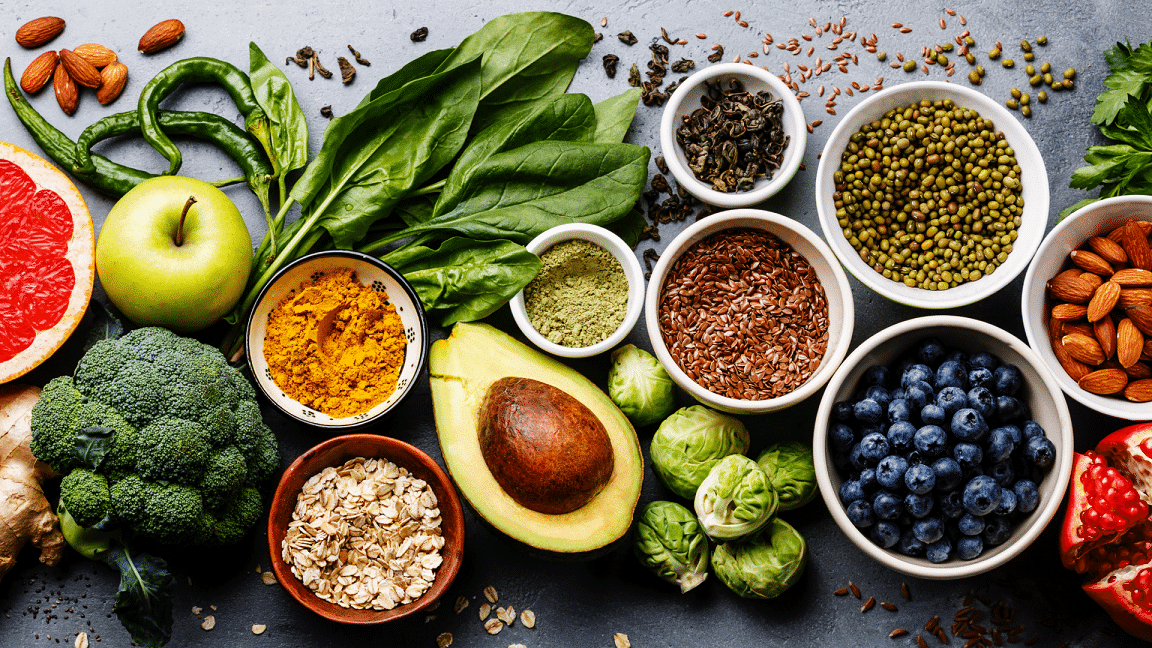
List Of Top 10 Foods Highest In Electrolytes
The following foods contain high levels of electrolytes and should be eaten if you’re experiencing any signs or symptoms of an imbalance.
Spinach
With a high concentration of sodium, calcium and magnesium, spinach is an electrolyte powerhouse. Since it’s also high in vitamin K and choline, it may help to reduce the risk of various cancers as well as osteoporosis (14).
Beets
High in potassium and with a moderate amount of sodium, beets are great for heart health and reducing the risk of stroke (27). If you don’t like beets, try making beet juice or toss them in a salad.
Tomatoes
Tomatoes are packed with potassium, calcium and magnesium and contain smaller amounts of sodium and phosphorus. They also contain vitamin C for immune health, A and B complex vitamins for various metabolic actions, antioxidants to fight cancer and heart disease, lycopene to reduce the risk of prostate cancer, lycopene to improve skin health, flavonoids for eye health and iron for oxygen transport (15).
Bananas
A great source of electrolytes are bananas. They have a high potassium content as well as some sodium and magnesium. Since they also contain vitamin B 6 for energy production, biotin for metabolism and hair health, try eating a banana if you feel tired or fatigued during the day (1).
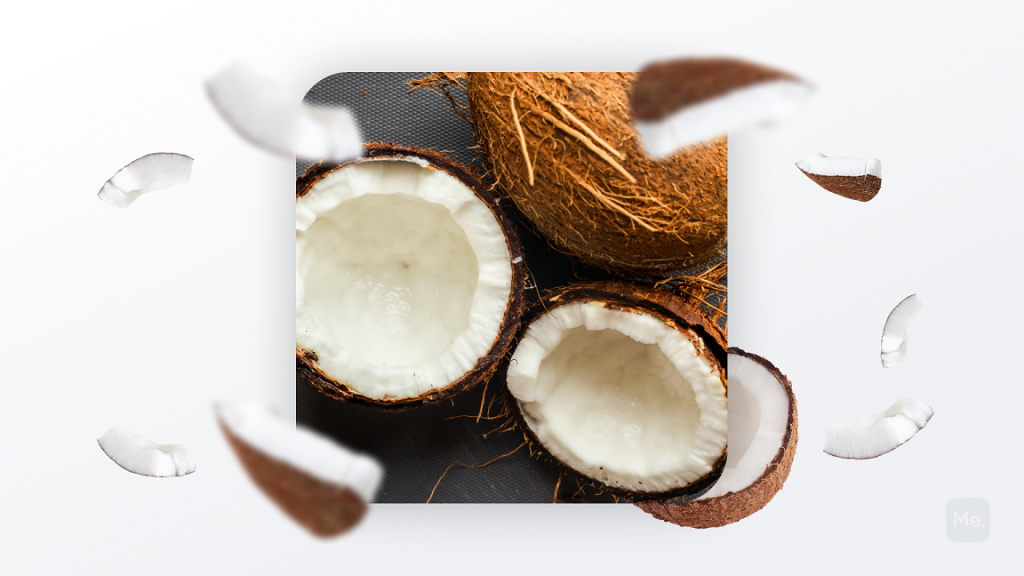
Coconut
Coconut contains a moderate quantity of potassium and is high in calcium and magnesium as well. It’s also rich in electrolytes, including sodium, phosphate and chloride. Coconut water can help to restore lost fluids during exercise or heat exposure, so it’s a great drink after strenuous activity or when you’re suffering from the effects of hot weather (4).
Almonds
Almonds are packed with minerals, including calcium for bone health, potassium for heart health and magnesium for energy production and electrolyte balance. Almonds also contain iron, B complex vitamins for metabolism as well as vitamin E to fight disease and inflammation (13).
Pumpkin Seeds
Loaded with minerals such as magnesium, manganese and phosphorus, pumpkin seeds are a great way to increase your intake of electrolytes. They’re also high in zinc for prostate health and vitamin K, which can reduce the risk of various forms of cancer (21).
Milk
Milk is high in electrolytes like calcium, potassium, phosphorus and magnesium. It’s also packed with B vitamins for energy metabolism as well as A and D vitamins to improve immune health (19).
Betterme will keep you laser-focused on your weight loss journey! Nutrient-packed meal plans, fat-blasting workouts, galvanizing challenges and much more. Try using the app and see for yourself!
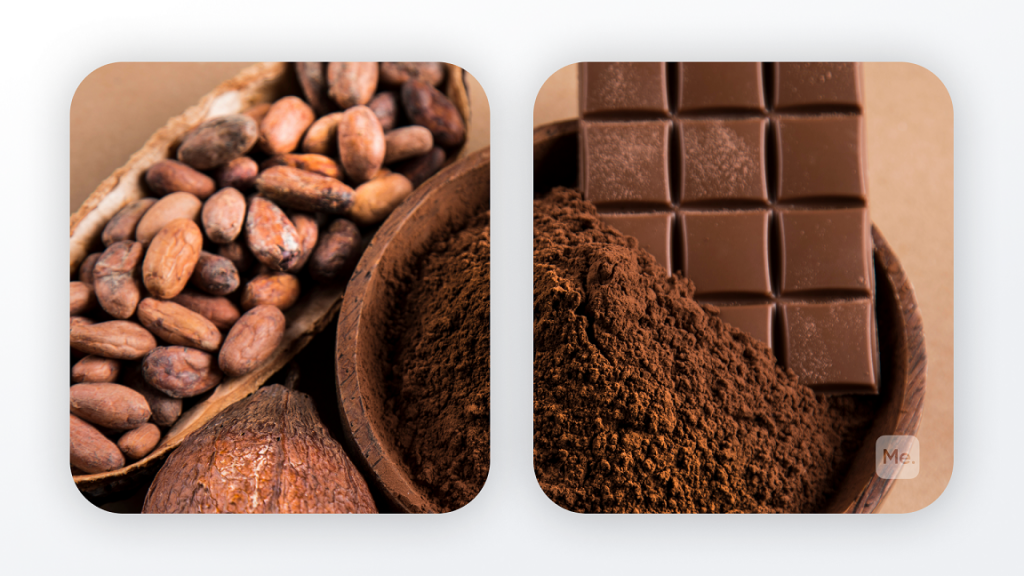
Cocoa
Chocolate might be high in calories, but it can be a healthy choice if you get dark chocolate or cocoa powder. These are high in calcium, magnesium and potassium as well as various antioxidants that can fight heart disease, cancer and other forms of disease (3).
Seaweed
Rich in iodine, seaweed or kelp can help to promote thyroid health. It also contains various minerals, including calcium, magnesium and iron. Since it’s rich in various antioxidants, seaweed is great for heart health as well (20).
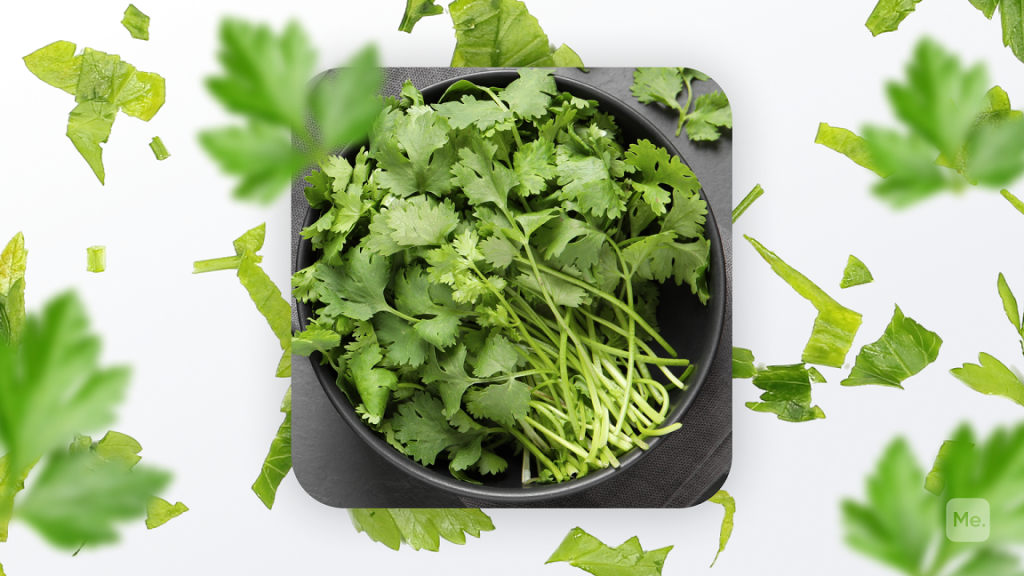
Cilantro
This herb is packed with nutrients like magnesium, manganese and potassium. It’s also a great source of calcium as well as vitamins A and C.
What Causes Electrolyte Imbalances?
Dehydration
The most common cause of electrolyte imbalances is dehydration (6). If you don’t drink enough water, your levels of sodium and other minerals can drop or rise to dangerous or even fatal levels. If you feel thirsty, you’re already dehydrated. Be sure to drink plenty of water throughout the day, and drink extra water when it is hot and when you exercise. You can lose both water and electrolytes through sweat, so if you are participating in an activity that causes you to sweat a lot, you may need to replace both water and electrolytes using either a commercially prepared or homemade oral rehydration solution.
Kidney Function
Another common cause of electrolyte imbalances is impaired kidney function. If your kidneys aren’t working properly due to an acute or chronic condition, you may have trouble excreting excess sodium, potassium, phosphate or other minerals (6).
Eating Disorders
Eating disorders like bulimia and anorexia can lead to problems with electrolyte balance as well. When these conditions involve vomiting after eating or laxative abuse, the body loses important electrolytes and minerals that are needed for cellular structure and function. In the case of anorexia or chronic undereating, the body doesn’t get in enough of those electrolytes in the first place, which often leads to imbalances.
Age
As you get older, your body might become less efficient at maintaining electrolytes in the blood. This means that elderly people should be especially careful about their intake of salt as well as foods high in sodium (9).
Diabetes
People with diabetes can be prone to electrolyte imbalances due to a variety of factors associated with their diabetes, such as impaired kidney function, malabsorption, acid-base disorders, and medication regimens (5). If you have diabetes, talk to your health care provider about signs to look out for and how to address electrolyte imbalances if they occur.
Medications
There are a number of medications that can cause problems with electrolytes. Kidney problems, heart failure and other conditions may require people to take diuretics, which make the kidneys release more water into the urine. Those who use these medications should regulate their intake of salt as well as potassium-rich foods like bananas and keep an open dialogue with their health care providers. Laxatives and other medications can cause problems with electrolyte balance as well (7).
Read More: 1200-Calorie Deficit: Is It A Safe Way To Lose Weight?
What Are The Signs Of Electrolyte Imbalance?
When the level of electrolytes in your body is too low or high, it causes symptoms such as:
Fatigue And Weakness
Common symptoms of low sodium levels are fatigue and weakness (12). When your body can’t produce enough energy due to an imbalance of electrolytes, it will try to preserve its resources by slowing down metabolism which then makes you feel fatigued all day long.
Muscle Cramps Or Spasms
Electrolytes also play a vital role in muscle contraction and nerve impulses. This is why having optimal levels maintains strength and flexibility. If there’s a lack of electrolytes, your muscles may either cramp or spasm (12).
Heart Palpitations And Irregular Heartbeat
When levels of potassium, calcium and magnesium decline rapidly it can lead to heart palpitations or irregular heartbeat which then causes shortness of breath and fainting. These symptoms are very similar to a recent myocardial infarction (heart attack). However, if you feel them after exercising for more than an hour they’re likely caused by electrolyte imbalance (12). This can be serious and requires medical attention.
Seizures And Fainting
Rapid shifts in water and/or sodium levels increase the risk for seizures or loss of consciousness (fainting). Usually, these serious symptoms appear when there’s a rapid decline or increase of sodium levels (12). If you have a seizure or loss of consciousness, medical attention is required.
Nausea And Vomiting
When you vomit, you lose both fluid and electrolytes. The lack of these nutrients causes an imbalance that makes you feel dizzy, weak and tired throughout the day (8).
Diarrhoea Or Constipation
Water and fluid are absorbed in the digestive tract. When things move too quickly, your body doesn’t get a chance to absorb them. In some cases, diarrhea even pulls fluid and electrolytes from the bloodstream back into the GI tract and they are then lost through the stool (8). Constipation, on the other hand, can be a sign of dehydration, which is a major contributor to electrolyte imbalance.
Heart Palpitations
If there’s a sudden decline in any level of calcium, potassium or magnesium, it can lead to heart palpitations which is one of the most common symptoms. Also, this is what happens when electrolytes are regulated too rapidly or they’re depleted quickly (12). If you experience heart palpitations, discuss it with your healthcare provider as you may need to be evaluated.
Irritability
When levels of magnesium are low you might feel more irritable or anxious due to lack of serotonin. Serotonin is a neurotransmitter that regulates mood and this decline can cause anxiety and depression (25).
BetterMe app will kick you out of the mental funk, shake off your extra weight, rid you off your energy-zapping habits, and help you sculpt the body of your dreams. Intrigued? Hurry up and change your life for the better!
Headaches
Electrolytes are able to regulate fluid balance in your brain which then reduces headaches. However, if there’s a rapid rise or decline the headache might cause the vision to blur and become sensitive to light (12).
Changes In Blood Sugar Levels
When levels of magnesium drop it affects insulin production which controls blood sugar levels. This increase or decrease can cause fluctuating energy levels, irritability, nausea or fatigue throughout the day (12).
Memory Loss
Low levels of potassium might trigger memory loss due to neurotransmitters that govern cognitive functions such as decision-making, memory retention and learning abilities (26).
How To Keep Your Electrolytes In Balance
The importance of electrolytes in the human body cannot be overemphasized. A number of common health problems are directly related to electrolyte imbalances. Additionally, the endocrine system relies on proper electrolyte balance for optimal function. Here are a few things you can do to ensure consistent balance:
Be Well-Hydrated
Drink at least six glasses of water per day. Water helps maintain proper hydration and prevents electrolyte imbalances by providing adequate minerals needed for reactions involving enzymes. You need to drink extra water if it is hot out or you are exercising. If you aren’t sure how much to drink, you can monitor your urine to gauge your hydration status – it should be pale yellow or clear, not dark and concentrated.
Don’t Drink Too Much Water
Drinking too much water in a short period of time may also cause electrolyte imbalances. This condition, known as hyponatremia, is caused by an overabundance of water relative to the amount of salt in the blood. Too much fluid dilutes essential minerals and can lead to dangerous or even fatal consequences if countermeasures are not taken (17). This is most likely to happen in a situation where you are losing both water and electrolytes (due to heavy sweating, vomiting, or diarrhea) and only replacing the water, but not the electrolytes. If you are losing water and electrolytes, it’s best to drink an oral rehydration solution instead of just plain water.
Eat Foods Rich In Electrolytes
It’s best to get your minerals from food whenever possible. Electrolytes found in whole foods have been paired with cofactors that help them function properly within the body.
Increase your intake of potassium-rich fruits, vegetables, beans, seeds or nuts daily (23). These foods are also high in B vitamins—particularly folic acid—and vitamin C which are essential cofactors responsible for protein metabolism and energy production.
Bananas are an excellent source of potassium as well as magnesium, a mineral that helps regulate calcium levels in the body. Vitamin B6 is necessary to convert tryptophan into niacin (vitamin B3) which enhances metabolic function and supports healthy bowel elimination (1).
Cut Back On Caffeine
Reduce sources of caffeine intake in your diet. Caffeine causes loss of water and important minerals through increased urination, therefore, affecting electrolyte concentrations (2).
Cut Back On Alcohol
Reduce sources of alcohol intake in your diet. Alcohol causes loss of water and essential minerals through increased urination resulting in altered electrolyte concentrations (24).
Cut Back On Salt
Avoid salty foods such as salted popcorn, chips, sausage, ham, corned beef, bacon and the like which are high in sodium chloride (salt). When combined with high carbohydrate snacks or beverages—like sugar or caffeine-containing soft drinks—this can result in an accelerated loss of potassium that may induce hypokalemia which can lead to muscle weakness/cramps and slow reflexes (16).
Don’t Overuse Diuretics Or Laxatives
Many over-the-counter medications, including diuretics and laxatives, can induce electrolyte imbalances. Consult your healthcare professional before using any medications to determine safe dosages and associated side effects.
Herbal supplements are not regulated by the FDA which means that it is possible they may interact with prescription medication or cause adverse reactions when taken together. It’s best to avoid any herbal supplements until you’ve talked with your healthcare provider.
Don’t Do Strenuous Exercise In Hot Weather
When you are dehydrated, your blood becomes more concentrated which increases the risk of developing hyponatremia (17). Strenuous exercise in hot weather can cause body fluid loss through perspiration. Ensure that you drink plenty of fluids before and after strenuous physical activity to prevent electrolyte imbalances due to dehydration or excessive salt loss.
Be Aware Of Certain Medical Conditions
A number of medical conditions may increase your chances of developing an electrolyte imbalance. These conditions include: diabetes, Addison’s disease, kidney disease, liver cirrhosis, Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis, certain endocrine disorders, wasting syndromes, malnutrition, metabolic alkalosis and certain cancers (8).
Consider Electrolyte Supplements
These supplements can help replenish essential minerals during times of increased loss due to vomiting, diarrhea, excessive perspiration or malabsorption. Electrolytes can also assist in restoring mineral balance following strenuous exercise (18). You can purchase supplements or commercially prepared electrolyte solutions, or make your own oral rehydration solution using a recipe based on the WHO’s recommended concentrations.
If you’ve been diagnosed with a specific electrolyte imbalance or medical condition, seek advice from your healthcare provider to determine whether using electrolytes supplements is right for you.
The Bottom Line
Electrolytes are minerals that carry an electrical charge. They’re vital for health and survival. If you are experiencing any symptoms of electrolyte imbalance, it’s important to consult your healthcare provider for advice on how to keep your electrolytes in balance.
Get your personalized
meal plan!
DISCLAIMER:
This article is intended for general informational purposes only and does not address individual circumstances. It is not a substitute for professional advice or help and should not be relied on to make decisions of any kind. Any action you take upon the information presented in this article is strictly at your own risk and responsibility!
SOURCES:
- Bananas (n.d., harvard.edu)
- Caffeine ingestion and fluid balance: a review (2003, pubmed.gov)
- Cocoa and chocolate in human health and disease (2011, nih.gov)
- Coconuts: Are there health benefits? (n.d., webmd.com)
- Diabetes mellitus and electrolyte disorders (2014, nih.gov)
- Electrolyte Disturbance and Acute Kidney Failure (n.d., medical.net)
- Electrolyte disturbance associated with medications in the critically ill (2012, researchgate.net)
- Electrolyte Imbalances + Normal Ranges and DIsturbances for Common Electrolytes (2021, ausmed.com)
- Electrolyte imbalances in an unselected population in an emergency department: A retrospective cohort study (2019, plos.org)
- Electrolytes (2021, medlineplus.gov)
- Fluid and Electrolyte Balance (2021, medlineplus.gov)
- General characteristics of patients with electrolyte imbalance admitted to emergency department (2013, nih.gov)
- Health benefits of almonds beyond cholesterol reduction (2012, pubmed.gov)
- Health Benefits of Spinach (2020, webmd.com)
- Health Benefits of Tomatoes (2017, psu.edu)
- Hypokalemia: A clinical update (2018, nih.gov)
- Hyponatremia: A practical approach (2014, nih.gov)
- Influence of Hydration and Electrolyte Supplementation on Incidence and Time to Onset of Exercise-Associated Muscle Cramps (2005, nih.gov)
- Milk and dairy products: good or bad for human health? An assessment of the totality of scientific evidence (2016, nih.gov)
- Nutritional and Digestive Health Benefits of Seaweed (2011, pubmed.gov)
- Nutritional and Therapeutic Effects of Pumpkin Seeds (2019, biomedres.us)
- Pathophysiology of water and sodium retention: edematous states with normal kidney function (2006, pubmed.gov)
- Potassium and Health (2013, nih.gov)
- The Diuretic Action of Weak and Strong Alcoholic Beverages In Elderly Men: A Randomized Diet-Controlled Crossover Trial (2017, nih.gov)
- The Expanded Biology for Serotonin (2018, nih.gov)
- The Link Between Potassium and Mild Cognitive Impairment in Mexican-Americans (2018, nih.gov)
- The Potential Benefits of Red Beetroots Supplementation in Health and Disease (2015, nih.gov)